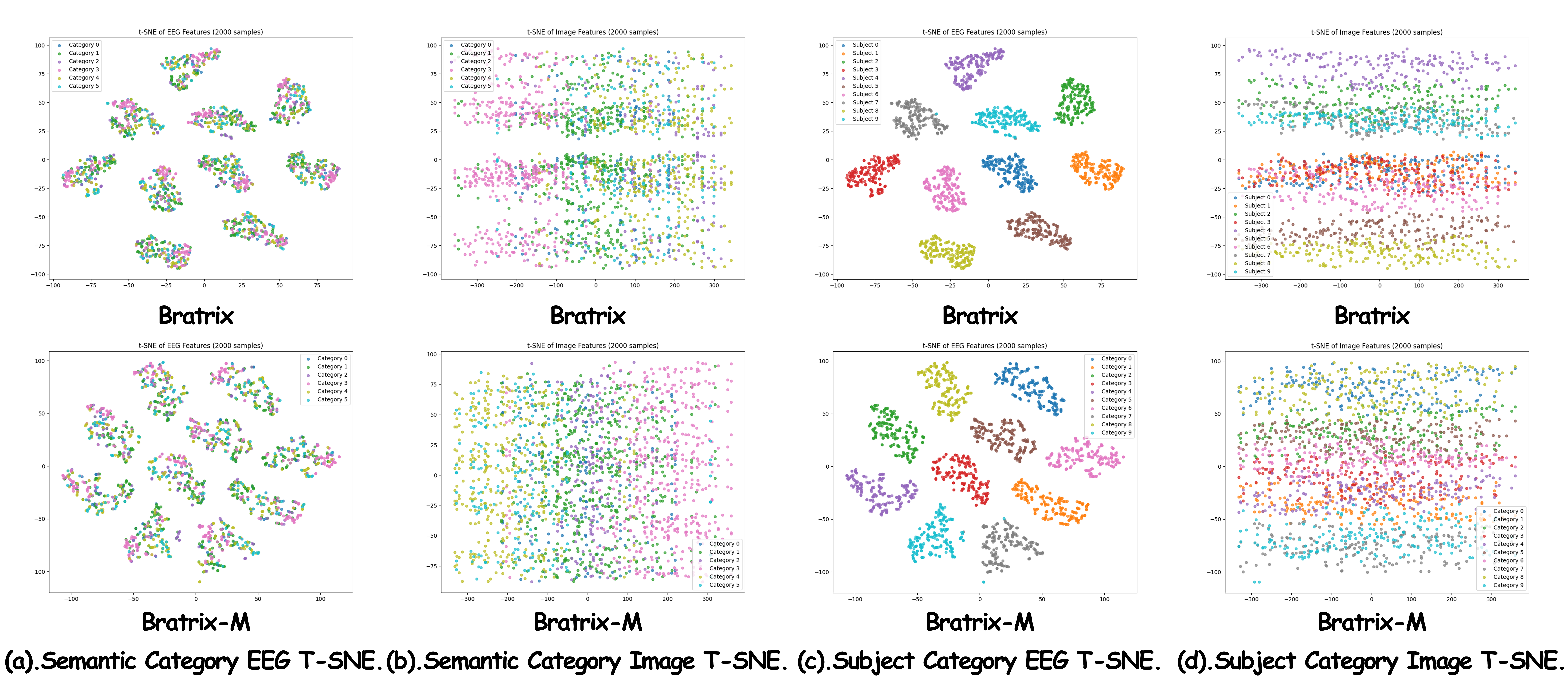
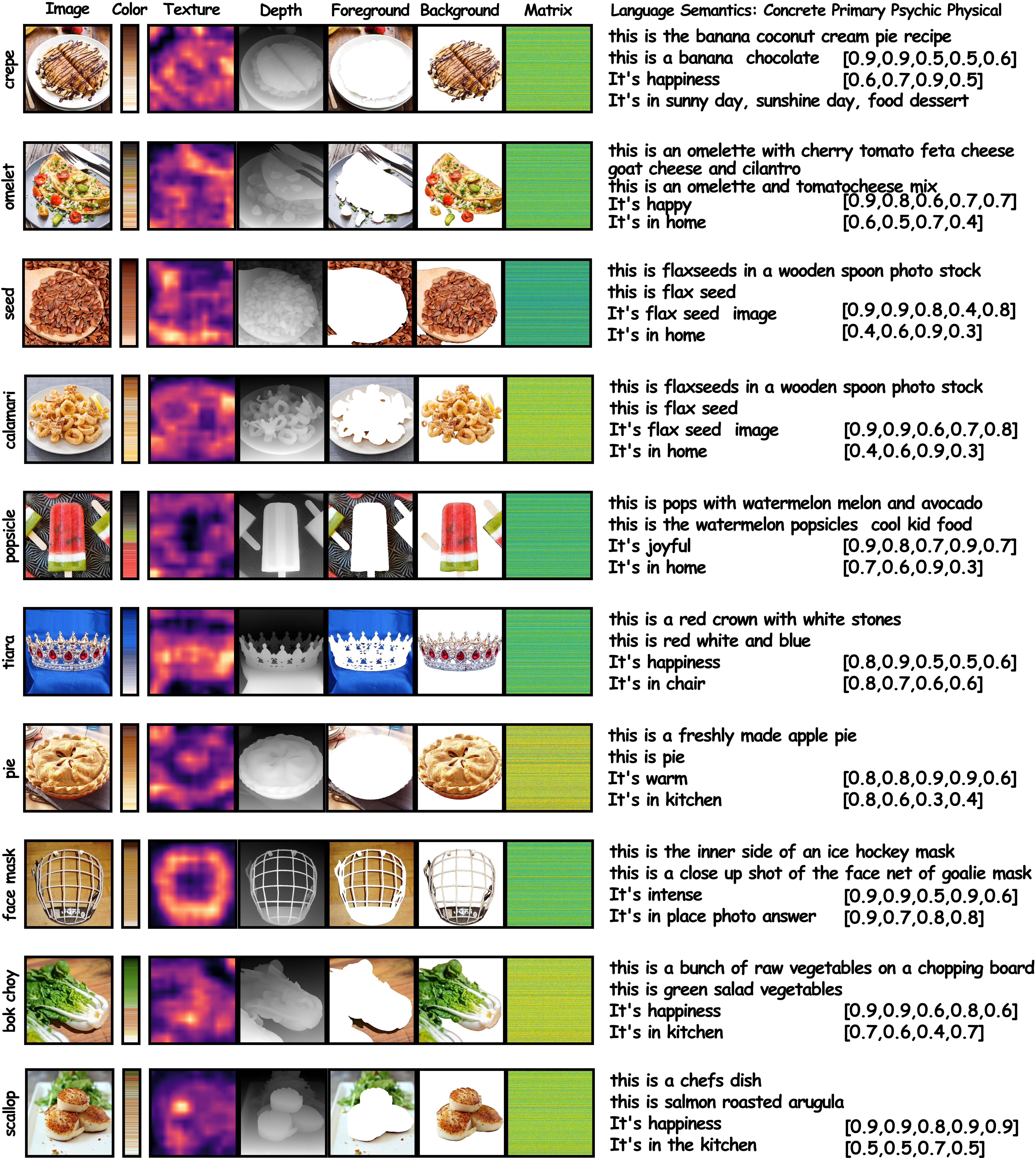
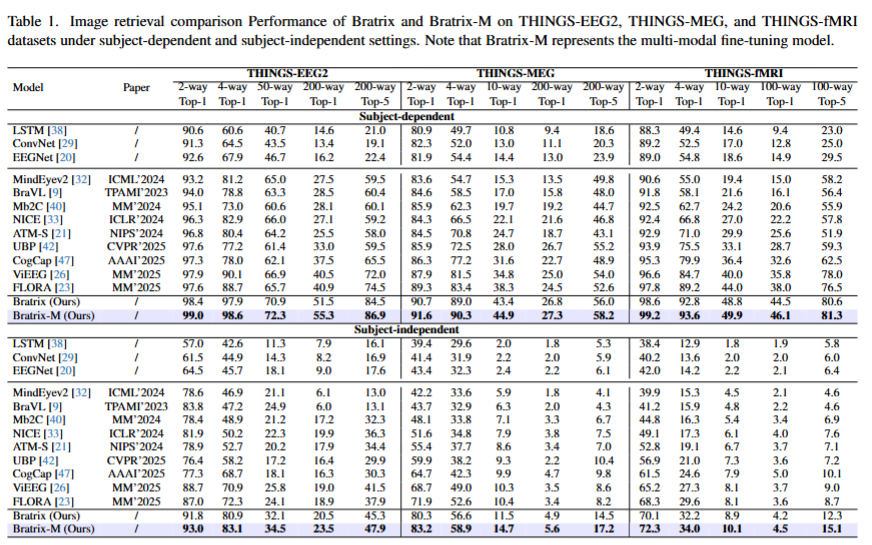
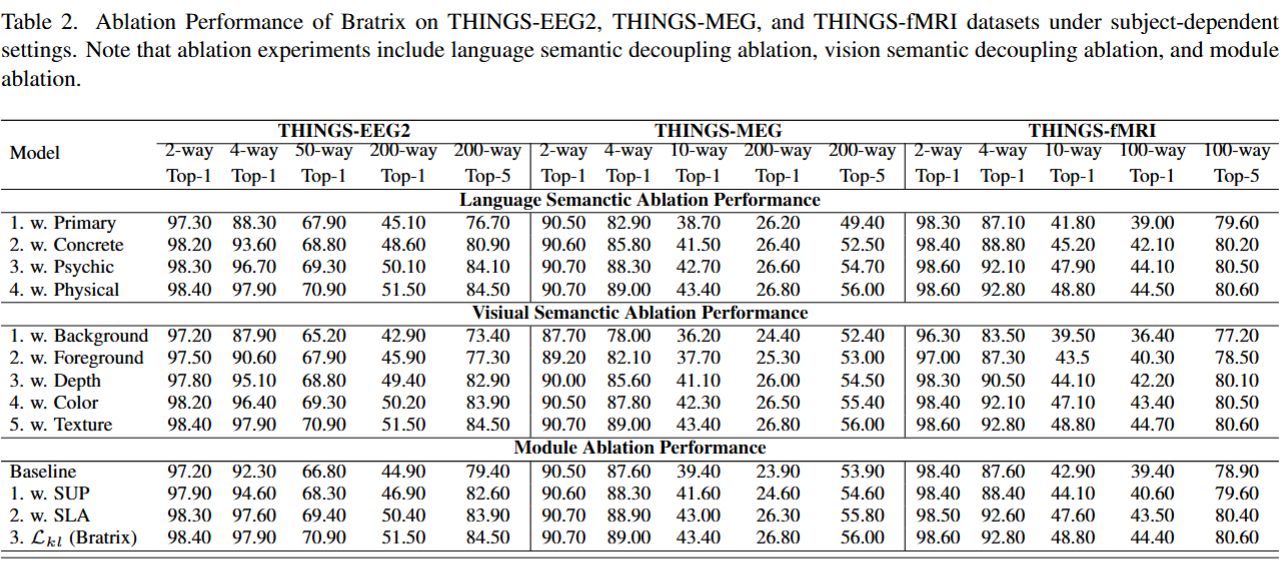
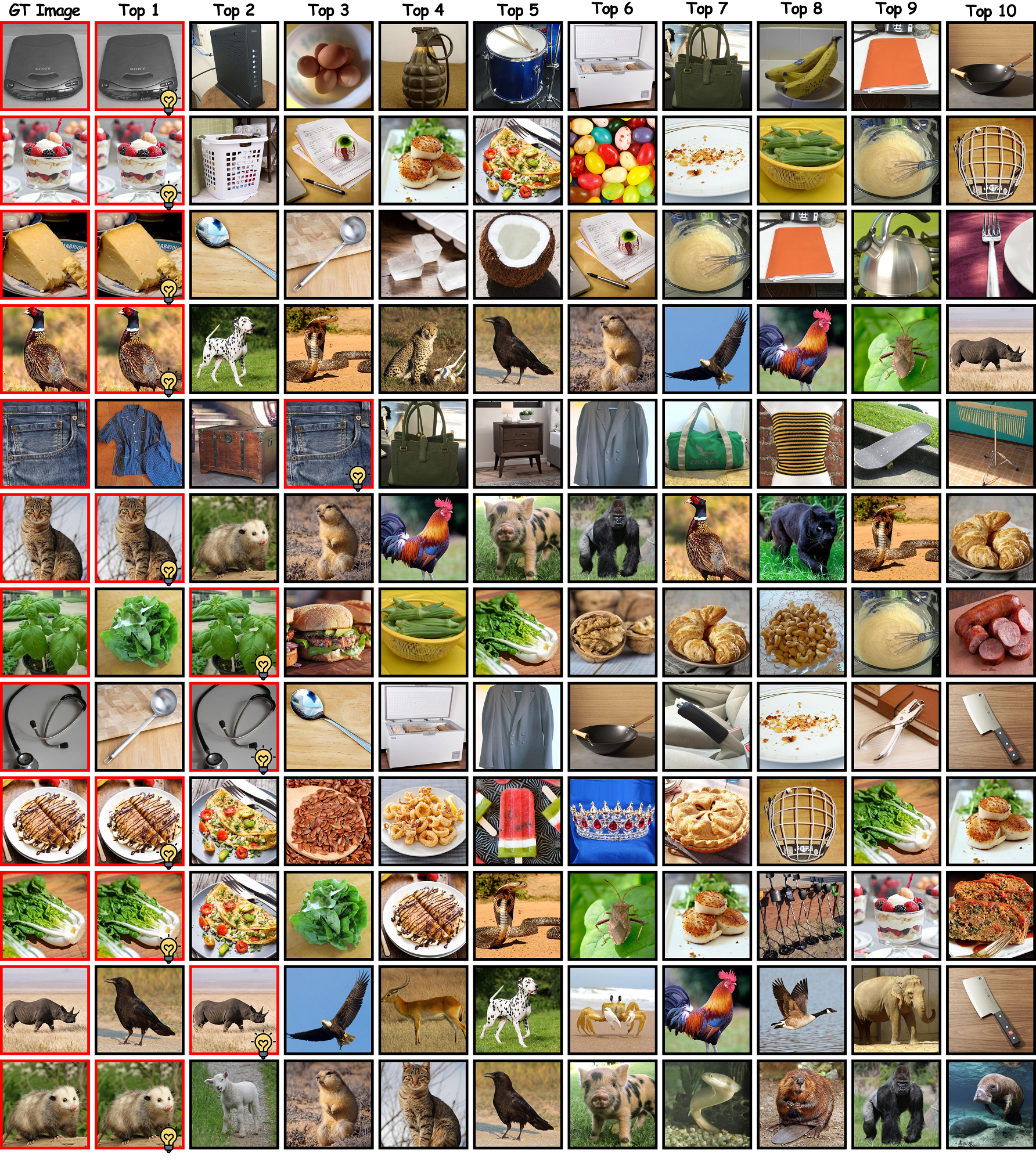
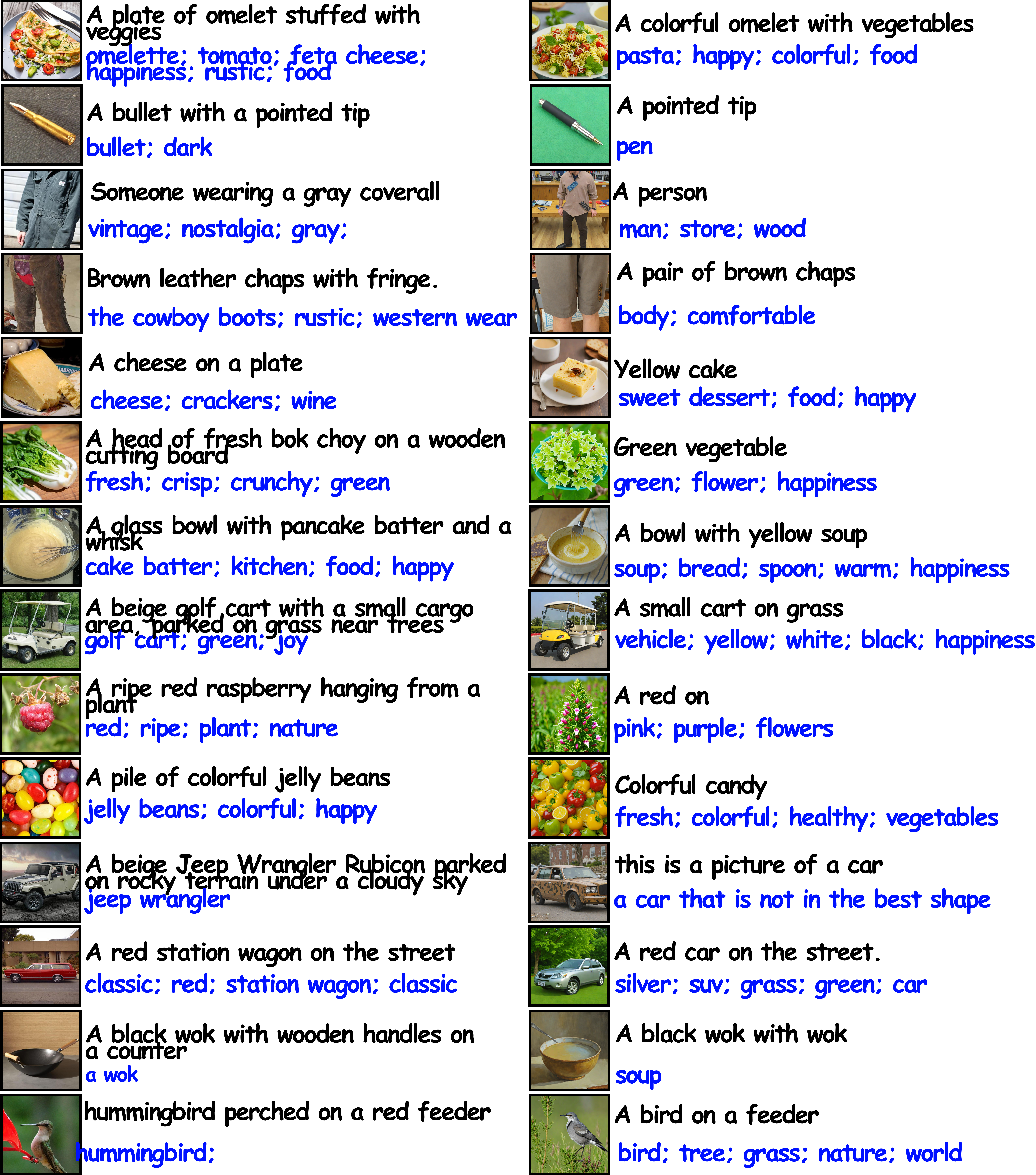
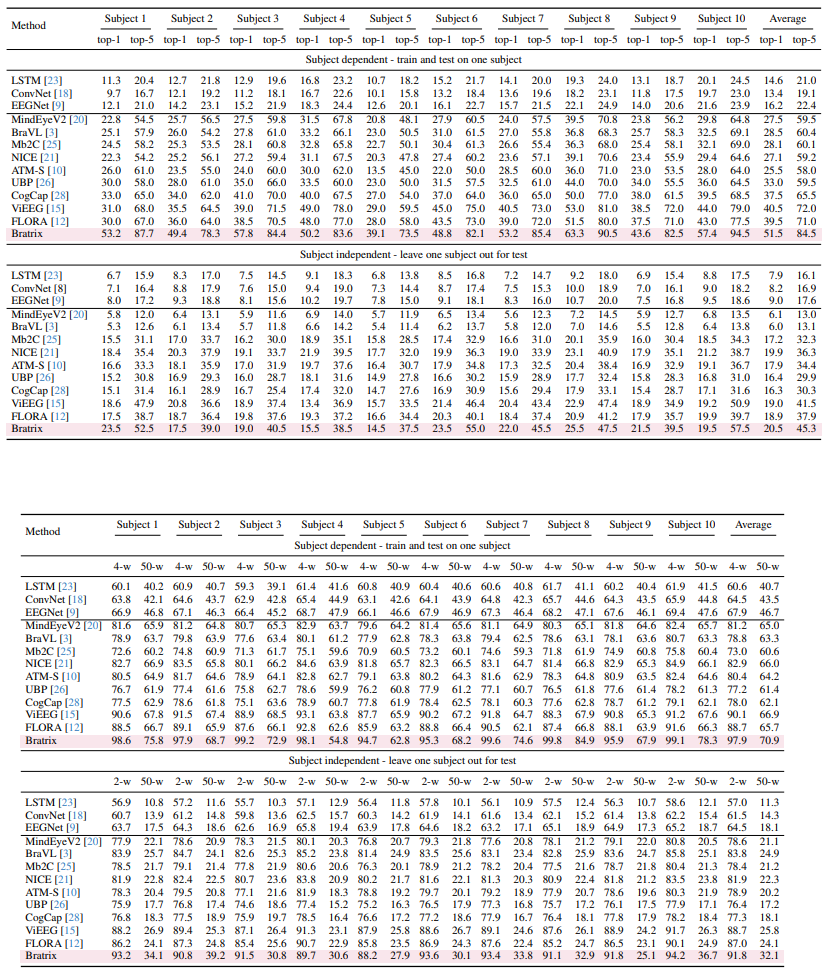
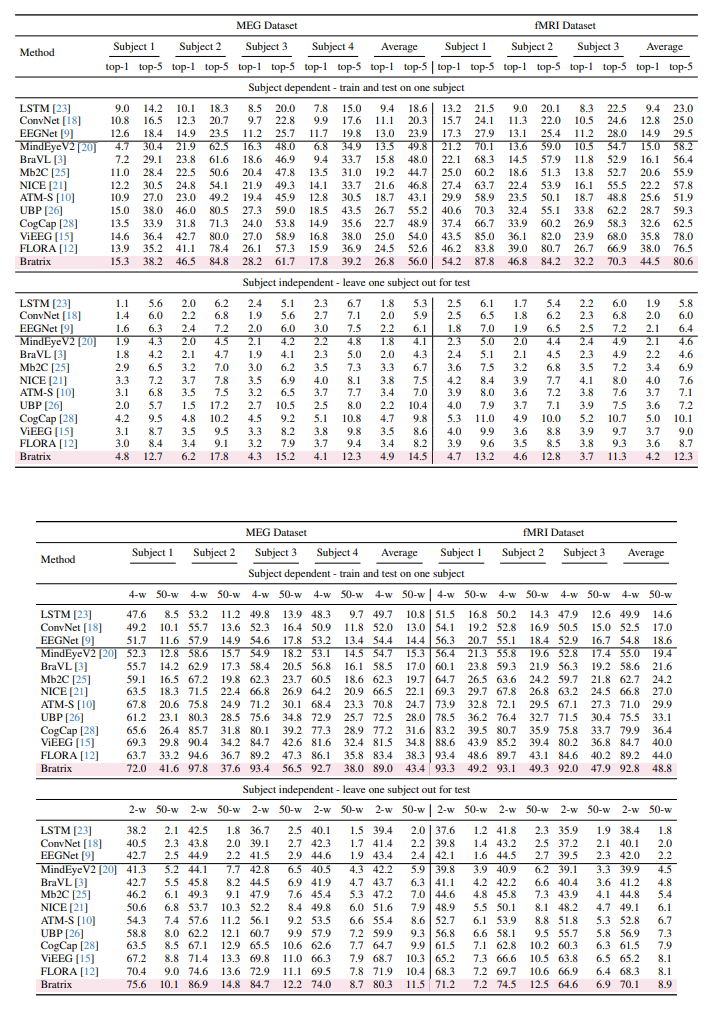
Unveiling visual semantics from neural signals such as EEG, MEG, and fMRI remains a fundamental challenge due to subject variability and the entangled nature of visual features. Existing approaches primarily align neural activity directly with visual embeddings, but visual-only representations often fail to capture latent semantic dimensions, limiting interpretability and robustness. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{Bratrix}, the first end-to-end framework to achieve Language-Anchored Vision–Brain alignment. Bratrix decouples visual stimuli into hierarchical visual and language semantic components and maps both visual and brain representations into a shared latent space, producing aligned visual–language and brain–language embeddings. To emulate human-like perceptual reliability and handle noisy neural signals, Bratrix incorporates a novel uncertainty perception module that applies uncertainty-aware weighting during alignment. By leveraging learnable language-anchored semantic matrices to enhance cross-modal correlations and employing a two-stage training strategy of single-modality pretraining followed by multimodal fine-tuning, \textbf{Bratrix-M} improves alignment precision. Extensive experiments on EEG, MEG, and fMRI benchmarks demonstrate that Bratrix substantially improves retrieval, reconstruction, and captioning performance compared to state-of-the-art methods, and that joint modeling in the multimodal semantic space further enhances brain–visual alignment. Code is publicly available
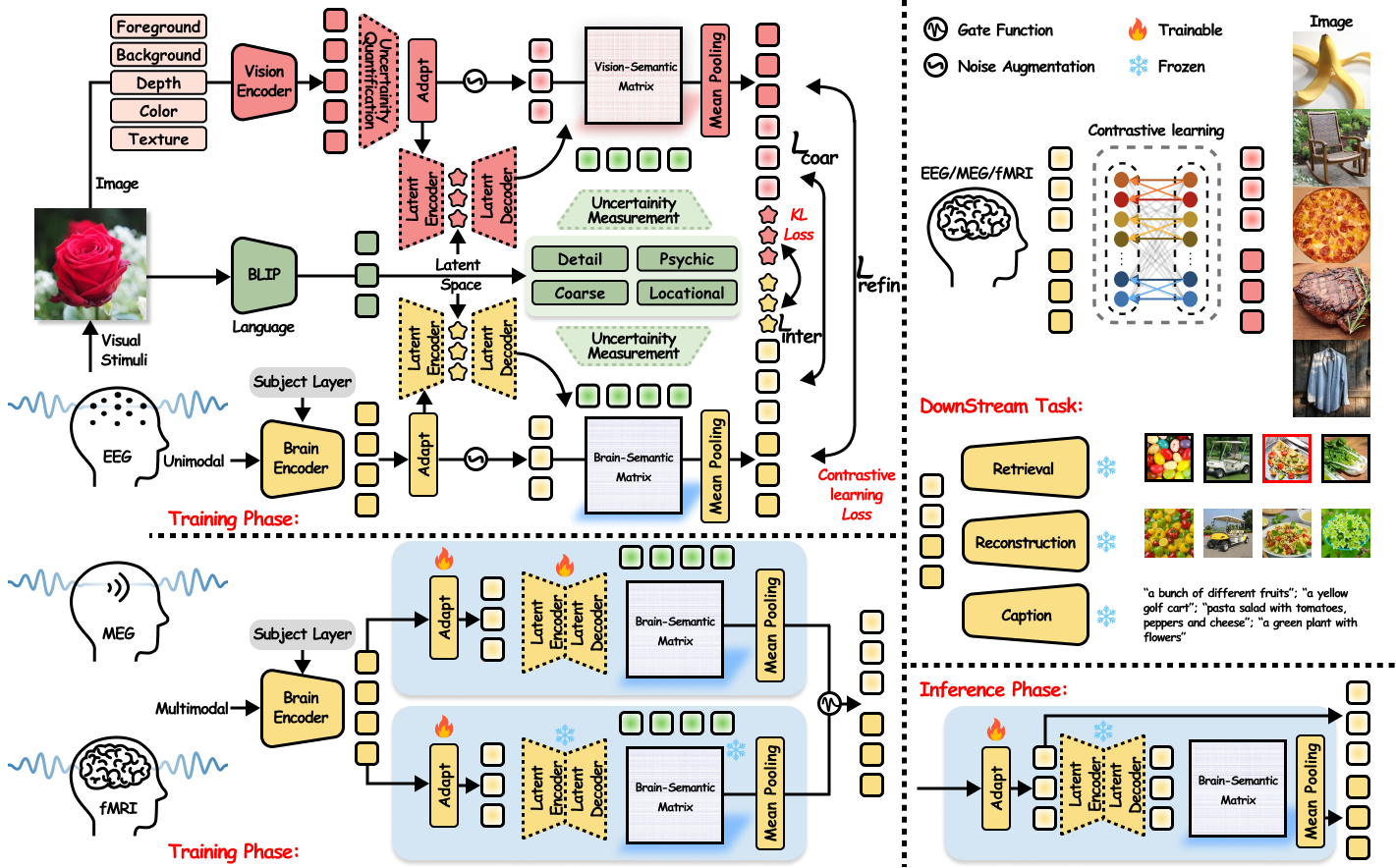
🌟🌟🌟 Overall Framework of Bratrix. Bratrix comprises Vision semantic decoupling pipeline, a Brain encoder pipeline, a language semantic decoupling pipeline, and a language-anchored visual-brain alignment.
🌟🌟🌟 There are totally four stages in this framework: single-modal per-training phase, multi-modal fine-tuning phase, inference phase, and downstream task phase.


@article{Bratrix,
title={Unveiling Deep Semantic Uncertainty Perception for Language-Anchored Multi-modal Vision-Brain Alignment},
author={Zehui Feng, Cuntai Guan, Ting Han},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:},
year={2025}
}